In medicine, exosome and stem cell therapy promise groundbreaking advancements in healing and tissue regeneration. These therapies offer a revolutionary approach to treating various medical conditions, harnessing the body’s innate mechanisms.
What Is Exosome and Stem Cell Therapy?
Exosome and stem cell therapy are innovative approaches in medicine that harness the body’s natural healing mechanisms to treat various medical conditions. Here’s a breakdown of each.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells with the remarkable ability to develop into various specialized cell types in the body. They serve as a repair system for the body, replenishing damaged or dying cells and tissues.
In stem cell therapy, stem cells are harvested from various sources, including embryonic tissue, fetal tissue, or adult tissues such as bone marrow or adipose tissue. These stem cells are then injected or implanted into the patient’s body at the site of injury or disease.
Once in the body, the stem cells can differentiate into the specific cell types needed for repair and regeneration, promoting tissue healing and functional restoration. Stem cell therapy has shown potential in treating a wide range of conditions, including musculoskeletal injuries, neurological disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune conditions.
Exosome Therapy
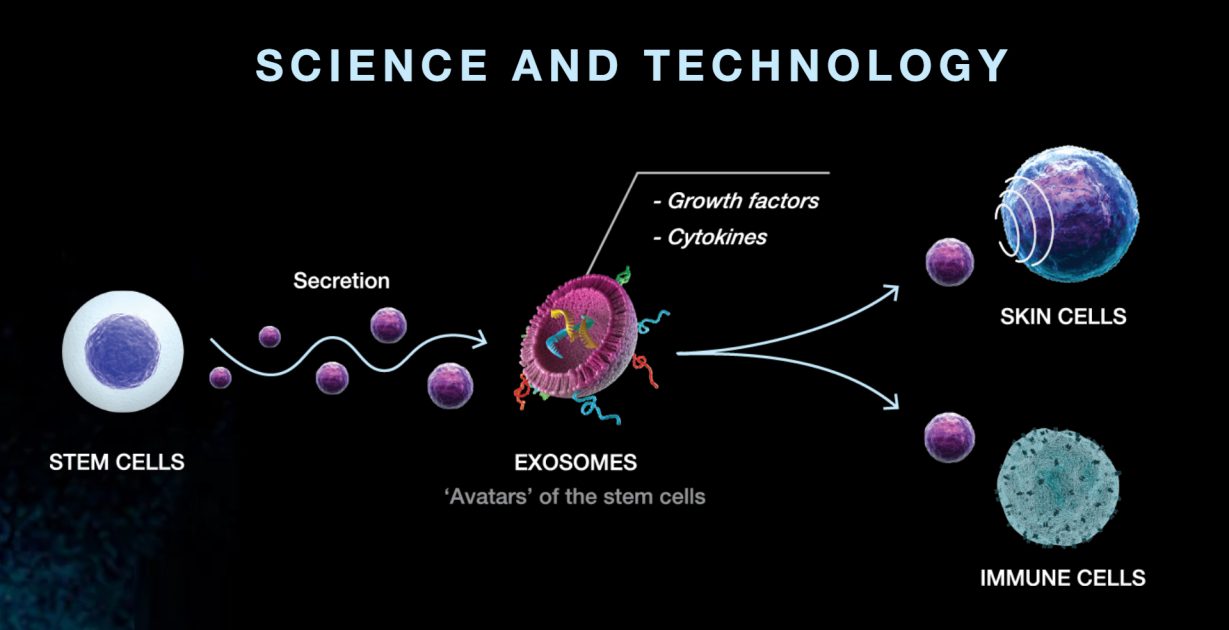
Exosomes are tiny vesicles secreted by cells, containing proteins, nucleic acids (such as RNA and DNA), lipids, and other bioactive molecules. These exosomes act as messengers, shuttling between cells to facilitate communication and regulate cellular processes.
In exosome therapy, exosomes are isolated from donor cells, typically stem cells, and administered to target tissues or organs to promote healing and regeneration.
This therapy has shown promise in treating conditions such as tissue injuries, degenerative diseases, and inflammatory disorders. It offers several advantages over traditional stem cell therapy, including easier storage and administration, reduced risk of immune rejection, and potentially fewer ethical concerns.

Difference Between the Two: Exosome vs. Stem Cell Therapy
Exosome therapy and stem cell therapy are two distinct approaches in regenerative medicine, each with unique mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications. Here are the key differences between the two:
Mechanism of Action
Exosome therapy involves the administration of extracellular vesicles, known as exosomes, which are derived from various cell types, including stem cells. Exosomes contain a cargo of bioactive molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and signaling molecules, which play crucial roles in intercellular communication and tissue repair.
These exosomes act as messengers, delivering therapeutic payloads to target cells and modulating cellular processes involved in regeneration, inflammation, and immune modulation.
In contrast, stem cell therapy entails the transplantation or infusion of stem cells, which possess the unique ability to differentiate into different cell types and replenish damaged tissues.
Stem cells can integrate into the host tissue, promote tissue regeneration through direct cell replacement, and exert paracrine effects by secreting trophic factors that modulate the local microenvironment and enhance tissue repair mechanisms.
Source and Preparation
Exosomes used in therapy can be derived from various cell sources, including mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), adipose-derived stem cells, and dendritic cells, among others. These exosomes are typically isolated from cell culture supernatants or biological fluids such as blood, urine, or amniotic fluid using specialized isolation techniques such as ultracentrifugation, size exclusion chromatography, or precipitation methods.
Once isolated, exosomes undergo purification and characterization to ensure their safety and efficacy for therapeutic use.
Stem cells used in therapy can be sourced from different tissue types, including embryonic tissue, fetal tissue, umbilical cord blood, bone marrow, adipose tissue, and peripheral blood. Stem cells are harvested from the donor tissue using minimally invasive procedures and then processed to isolate and concentrate the desired cell population for transplantation.
Clinical Applications
Exosome therapy shows promise in treating inflammatory disorders, autoimmune diseases, tissue injuries, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disorders, and wound healing, among others. Exosomes’ ability to modulate immune responses, promote tissue regeneration, and mitigate inflammation makes them attractive candidates for therapeutic intervention.
Stem cell therapy, on the other hand, has been investigated for a wide range of conditions, including musculoskeletal injuries, neurological disorders, cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune conditions, and aesthetic procedures. Stem cells’ regenerative potential, ability to differentiate into multiple cell types, and paracrine effects contribute to their efficacy in promoting tissue repair and functional restoration in various clinical settings.
Benefits of Exosome and Stem Cell Therapy
Exosome and stem cell therapies are revolutionizing regenerative medicine with their ability to harness the body’s natural healing mechanisms. These therapies offer numerous benefits, including minimal invasiveness, reduced risk of rejection, versatility across medical specialties, and the potential for personalized treatment.
Regenerative Potential
These therapies harness the body’s natural regenerative mechanisms to promote tissue repair and regeneration. Stem cells can differentiate into various cell types, replenishing damaged or diseased tissues.
Exosomes, on the other hand, contain a cargo of bioactive molecules that stimulate cellular processes involved in tissue healing. With these regenerative properties, exosome and stem cell therapies offer the potential to restore tissue function and improve patient outcomes.
Minimally Invasive
Stem cell and exosome therapies are often minimally invasive procedures, involving injections or infusions of therapeutic agents directly into the target tissues or organs.
Compared to surgical interventions, which may carry greater risks and longer recovery times, exosome and stem cell therapies offer a less invasive alternative for patients. This minimally invasive approach reduces the likelihood of complications, accelerates recovery, and enhances patient comfort.
Reduced Risk of Rejection
Exosome therapy, in particular, offers the advantage of using cell-free vesicles derived from donor cells, reducing the risk of immune rejection. Because exosomes lack cell surface antigens, they are less likely to trigger immune responses or provoke graft-versus-host reactions in recipients.
This mitigates concerns associated with tissue compatibility and immunogenicity, making exosome therapy a potentially safer option for patients requiring regenerative treatments.
Versatility
Exosome and stem cell therapies have broad applications across various medical specialties and conditions. From musculoskeletal injuries to neurological disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and aesthetic enhancements, these therapies offer versatile solutions for a wide range of clinical scenarios.
Potential for Personalized Medicine
Exosome and stem cell therapies hold promise for personalized medicine approaches, where treatments can be customized based on individual patient characteristics and disease profiles. By harnessing the regenerative capabilities of exosomes and stem cells, clinicians can develop targeted therapies tailored to the unique needs of each patient.
This personalized approach maximizes treatment efficacy, minimizes adverse effects, and optimizes patient outcomes, representing a paradigm shift toward precision medicine in regenerative medicine.
Practical Applications of Exosome and Stem Cell Therapy in Regenerative Medicine
Exosome and stem cell therapy hold immense promise in revolutionizing the landscape of regenerative medicine, offering novel approaches to treat a wide range of diseases and injuries. Here are some practical applications of these therapies:
Musculoskeletal Injuries
Stem cell and exosome therapy hold significant promise in the treatment of musculoskeletal injuries such as tendon and ligament tears, osteoarthritis, and muscle strains. Stem cell injections have been used to promote tissue repair and regeneration in damaged joints, tendons, and cartilage, potentially offering a non-surgical alternative for patients suffering from these conditions.
Exosome therapy, either alone or in combination with stem cells, has shown efficacy in enhancing the healing process, reducing inflammation, and improving functional outcomes in musculoskeletal injuries, as per studies.
Neurological Disorders
According to research, stem cell transplantation holds promise for conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, spinal cord injuries, and stroke. Stem cells have the potential to replace damaged neurons, promote neurogenesis (the formation of new neurons), and modulate inflammatory responses in the central nervous system.
Exosomes derived from stem cells also exhibit neuroprotective and neurodegenerative properties, making them attractive candidates for the treatment of neurological conditions.
Cardiovascular Diseases
Stem cell and exosome therapy offer innovative approaches for treating cardiovascular diseases, including myocardial infarction (heart attack), heart failure, and peripheral artery disease. Stem cell transplantation has been investigated as a means to regenerate damaged heart tissue, improve cardiac function, and promote angiogenesis in ischemic regions.
Exosomes derived from stem cells contribute to cardioprotection by delivering cardioprotective factors, promoting angiogenesis, and reducing inflammation in the heart. These therapies hold promise for improving outcomes in patients with cardiovascular diseases.
Aesthetic Enhancements
In the field of aesthetic medicine, exosome and stem cell therapy are gaining traction for their potential in aesthetic plastic surgery to rejuvenate skin, promote hair growth, and enhance tissue regeneration.
Stem cell-based therapies are being explored for facial rejuvenation, scar reduction, and hair restoration, leveraging the regenerative properties of stem cells to improve skin texture, tone, and elasticity.
Exosome therapy is also being investigated for its ability to stimulate collagen production, promote wound healing, and improve the overall appearance of the skin. These treatments offer minimally invasive options for patients seeking cosmetic enhancements.
Orthopedic Conditions
Stem cell and exosome therapy show promise in the management of orthopedic conditions such as bone fractures, cartilage defects, and spinal disc degeneration. Stem cell injections have been used to promote bone healing and repair in non-union fractures and critical-sized defects.
Exosome therapy has also demonstrated efficacy in enhancing cartilage regeneration and reducing inflammation in conditions such as osteoarthritis.
These therapies offer potential alternatives to traditional orthopedic interventions to improve outcomes and quality of life for patients with musculoskeletal disorders.
Controversies and Regulatory Landscape
Despite their promising potential, exosome and stem cell treatments have sparked debates and raised concerns on several fronts, prompting regulatory bodies to establish guidelines and oversight. Here’s an exploration of the controversies and regulatory landscape surrounding exosome and stem cell therapy:
Regulatory Oversight and Enforcement
Regulatory oversight of exosome and stem cell therapy varies by jurisdiction, with different countries implementing varying degrees of regulation.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has taken steps to regulate stem cell therapies and exosome products, particularly those considered to be biological drugs or subject to the same regulatory framework as drugs.
However, enforcement of regulations in this rapidly evolving field remains challenging, leading to instances of non-compliance and regulatory violations by some clinics and practitioners.
Safety and Efficacy Concerns
Another area of concern revolves around the safety and efficacy of exosome and stem cell therapy. While there is growing evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of these treatments, their long-term safety and efficacy profiles remain largely uncharted territory.
Questions persist regarding the potential risks associated with stem cell transplantation, such as tumor formation, immune rejection, and unintended differentiation. Moreover, the variability in exosome isolation and characterization methods raises questions about the consistency and reliability of exosome-based therapies.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are also considered, particularly regarding the sourcing and use of stem cells. Issues such as informed consent, patient autonomy, and the ethical implications of using embryonic stem cells or fetal tissue for research and treatment raise complex ethical dilemmas.
Additionally, concerns about the commercialization of stem cell therapies and the exploitation of vulnerable patients underscore the need for ethical guidelines and safeguards in this field.
Need for Evidence-Based Practice
Although there are studies about exosome and stem cell therapy, there is a limited amount of research on these regenerative treatments.
Rigorous clinical research, randomized controlled trials, and long-term follow-up studies are essential to establish the safety, efficacy, and optimal use of these treatments. Transparency, peer review, and adherence to ethical standards ensure that exosome and stem cell therapies fulfill their promise as legitimate and beneficial medical interventions.
The Potential for Further Research and Utilization
While challenges exist, the landscape of exosome and stem cell therapy is ripe with opportunities for further exploration and utilization. Ongoing research endeavors seek to unravel the intricacies of exosome biology, optimize stem cell-based approaches, and elucidate their full therapeutic potential.
With continued scientific inquiry and regulatory oversight, these therapies hold the promise of revolutionizing healthcare, offering new avenues for healing and regeneration.
Consider Exosome and Stem Cell Therapy Today
Exosome and stem cell therapy offer a holistic approach to healing that taps into the body’s natural regenerative mechanisms. While controversies and regulatory challenges persist, the immense potential for further research and utilization underscores the transformative impact of these therapies.
As science continues to unravel its mysteries, the future holds immense promise in exosome and stem cell therapy to pave the way for a healthier tomorrow.
We offer various regenerative medicine services for a wide range of conditions. Take the first step toward rejuvenating your health and vitality by scheduling an appointment with our broad certified medical provider today.












4 Responses
Hey there, You have done a fantastic job. I will certainly digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m confident they’ll be benefited from this site.
Your writing is not only informative but also incredibly inspiring. You have a knack for sparking curiosity and encouraging critical thinking. Thank you for being such a positive influence!
Hello! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back frequently!
Usually I do not read article on blogs however I would like to say that this writeup very compelled me to take a look at and do it Your writing style has been amazed me Thank you very nice article